Monday, January 14, 2008
Facilitator's Question
There are different constraints and limitations when using cranes for material handling, depending on the models of crane used.
Here are some constraints and limitations of most cranes:
- Cost
The costs of setting up cranes in warehouses are very expensive. Therefore, the company has to make a solid decision whether cranes are needed for their operations. Any wrong decision made might have a great impact on the company.
- Not able to move a heavy flow of volume like conveyor does.
Cranes are only able to move goods one at a time, discontinuously. As compared to conveyors which move goods continuously. This could slow down operation time and affect the total production of the company.
- Space utility.
With the usage of cranes in warehouses, the space utilized will not be exactly 100%. This is because certain cranes need some space to move, like the radius from the pivot to the material. This will definitely decrease the storage space in the warehouse. Therefore, the warehouse might be better off not using cranes, increasing space utiization for the goods.
- Stability of crane.
For the crane to be stable, the maximum lifting capacity of the crane has to be taken into serious consideration. Failure to comply may result in the crane tipping over, due to over-lifting. Serious accidents may occur if the crane tips over.
- Need for certification.
As cranes accidents can be very fatal and dangerous, and not everyone is able to operate cranes well, finding a skilled and experienced crane operator may be a concern. In some regions, the crane operators licence may be needed, hence companies have toeither hires certified operators or send their employees to be trained and certified.
- Regular checks required.
Regular checks need to be conducted on the cranes to ensure that the equipments are in good working condition, which would mean machine downtime, affecting operations unless company has another machine to stand-by for such cases. Any malfunctioning parts will need to be replaced immediately, without further delay. Failure to do so, might have undesirable consequences in future.
Friday, January 11, 2008
4) Stacker Cranes
These cranes are usually used for storing and retrieving unit loads in storage racks, especially in high-rise applications in which the racks are more than 50 feet high.
The crane can be either controlled remotely or by an operator in a cab on the mast.
Below are some pictures of stacker cranes:
1) Operator-controlled

2) Remotely-controlled

3) Bridge Cranes
An “overhead” bridge crane is better suited for transporting heavier loads, whereas an “underhung” bridge crane is more suitable to carry lighter loads.
An “underhung” bridge crane has an advantage, whereby it can transfer loads and interface with other material handling equipments, such as monorail systems. In this way, goods can be transferred without wasting too much manpower’s effort.
Below are pictures of bridge cranes:
1) Underhung Bridge Crane
.jpg)
2) Overhead Bridge Crane
.jpg)
2) Jib Cranes
A hoist is attached to the arm for lifting. The hoist can move along the arm, to lift the goods from one place to another. The arm can be mounted onto the wall or to the floor as support, and it can rotate 360°.


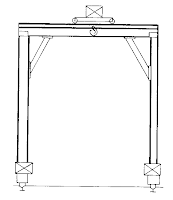
1) Gantry Crane
For single and double leg cranes, the legs of the cranes are in a fixed position and it is secured tightly onto the floor.
For mobile gantry cranes, they are self-supporting and travel directly on the floor. The cranes are operated by power drives, which act as wheels. In this way, these cranes can be moved from one location to another easily.
The 4 pictures below shows the different types of gantry cranes available:
1) Single Leg (fixed)

2) Double Leg (fixed)
.gif)
3) Double Leg (Mobile)

4) Power drives for mobile gantry cranes

Cranes
- Used to move loads over variable (horizontal and vertical) paths within a restricted area.
- Used when there is insufficient (or intermittent) flow volume such that the use of a conveyor cannot be justified.
- Provide more flexibility in movement than conveyors.
- Provide less flexibility in movement than industrial trucks.
- Loads handled are more varied with respect to their shape and weight than those handled by a conveyor.
- Most cranes utilize hoists for vertical movement, although manipulators can be used if precise positioning of the load is required.
There are various types of cranes being used in the logistics industry. For our project, we are focusing on 4 types of cranes, which are:
1) Gantry Cranes;
2) Jib Cranes;
3) Bridge Cranes;
4) Stacker Cranes.
The types of cranes and their uses will be explained further in the following entries on cranes.
All of our information on cranes are sourced from these websites:
Cited from:
http://www.ise.ncsu.edu/kay/mhetax/TransEq/Crane/index.htm
http://www.lkgoodwin.com/cgi-bin/quikstore.cgi?category=Cranes_-_All_Types
Thursday, January 10, 2008
Pallet Jacks (Extra information...)

Below are additional information on Industrial trucks: 2
- Used to move materials over variable (horizontal) paths with no restrictions on the area covered (i.e., unrestricted area)
- Provide vertical movement if the truck has lifting capabilities
- Used when there is insufficient (or intermittent) flow volume such that the use of a conveyor cannot be justified
- Provide more flexibility in movement than conveyors and cranes
- Not licensed to travel on public roads—"commercial trucks" are licensed to travel on public roads
Pallet jacks are also used for external distribution operations, where 1 or 2 pallet jacks are usually kept in the trucks that are used for distribution of materials. 3
While pallet jacks are common equipment used in Distribution Centres, there are still limitations. Here are some points to note when deciding on pallet jack usage.
Restrictions: 1
- Reversible pallets cannot be used.
- Double-faced non-reversible pallets cannot have deckboards where the front wheels extend to the floor, and enables only two-way entry into a four-way notched-stringer pallet because the forks cannot be inserted into the notches
- Operate only on one level. 4
Advantages: 4
- Excel at picking bulky or full case items.
- Can travel fast (twice the speed of a person) and can carry a large load.
- Can add an extra long fork and carry two pallets at once.
- Very versatile and can pick order, load trucks, or transport pallets from one place to another.
- Equipment ranges from manual jacks to powered equipment that the operator rides.
In conclusion to our pallet jack posts, we can see that there is a big variety of pallet jacks in the market nowadays due to the constantly changing and improving technology.
Instead of the traditional manual pallet jacks, customers can now choose from multiple catergories under pallet truck types. One example taken from LK Goodwin Co. 5 would be classifying pallet trucks under,
1. Hand Propelled Pallet Trucks
2. High Lift and Tilting Pallet Trucks
3. Special Purposes Pall et Trucks
et Trucks
For more information, we hope that the sources stated will be able to help. Other wise, leave us a message and we'll get back ASAP.
Sources:
1-http://www.ise.ncsu.edu/kay/mhetax/TransEq/IndusTr/index.htm#Pallet%20jack
2-http://www.ise.ncsu.edu/kay/mhetax/TransEq/IndusTr/index.htm#Pallet%20jack
3- Temasek Business School, Diploma in Logistics and Operations Management, Transport Management, AY2007/2008, April Semester, Students’ Note, Lecture 11
4- http://www.2wmc.com/Companion/KnowledgeVehicles.html
5-http://www.lkgoodwin.com/cgi-bin/quikstore.cgi?category=Pallet_Trucks_-_All_Types
Pallet Jacks in the market - Powered
1. Electric Pallet Truck Model XPT30 Series 1
- Lift ram is hard chromed plated for long life and mounted for even load lifting. Pump unit, motor and solenoid actuated, pressure compensated lowering valve is easily accessible.
Hydraulic/ Controller/ Electrical System:
- Lift ram is hard chromed plated for long life and mounted for even load lifting. Pump unit, motor and solenoid actuated, pressure compensated lowering valve is easily accessible.
4. Fully Powered Electric Pallet Trucks 4
 - Easy and quick operation. Includes fingertip raise and lower buttons. Easy-to-operate throttle for forward and reverse direction offers infinite speed selection.
- Easy and quick operation. Includes fingertip raise and lower buttons. Easy-to-operate throttle for forward and reverse direction offers infinite speed selection.Sources:
1 –http://www.lkgoodwin.com/more_info/series_xpt30_electric_pallet_truck/series_xpt30_electric_pallet_truck.shtml
2- http://www.lkgoodwin.com/more_info/series_xpt45_electric_pallet_truck/series_xpt45_electric_pallet_truck.shtml
3-http://www.lkgoodwin.com/more_info/electric_pallet_truck_eme/electric_pallet%20truck_eme.shtml
4- http://www.pallet-jack.org/Vestil-Electric-Pallet-Jacks.htm
Pallet Jack models in the market - Manual
Here are some models available in the current market:
1. Wheel Nose Pallet Jack 1  - Designed to position pallets or skids closely in a row, it includes two articulating steering wheels and two front load rollers. The fork end is set back from front rollers allowing for one pallet pick up at a time
- Designed to position pallets or skids closely in a row, it includes two articulating steering wheels and two front load rollers. The fork end is set back from front rollers allowing for one pallet pick up at a time
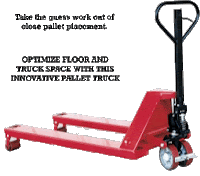 - Rubber grip handle with 3 lever position for easy operation and maneuvering. Spring loaded loop handle automatically returns to vertical position.
- Rubber grip handle with 3 lever position for easy operation and maneuvering. Spring loaded loop handle automatically returns to vertical position.
Capacity: 5,000 pounds
Fork dimensions: Extra long 45" forks used with standard 48" long pallets, short 38" forks used for maneuvering in tight spaces.
Service range: 3-1/2" to 8"
2. ML55SS 2 - specially built with heavy-duty(high tensile strength) top quality galvanized stainless steel to guarantee super performance and durability in tough environments. All stainless steel construction meets sanitary requirements for food, medical and pharmaceutical industries
- specially built with heavy-duty(high tensile strength) top quality galvanized stainless steel to guarantee super performance and durability in tough environments. All stainless steel construction meets sanitary requirements for food, medical and pharmaceutical industries
- assures longer usage in wet, cold and corrosive environments or in the chemical, fishing and meat-processing industries.
- manufactured & tested to meet ISO 9002 & TUV/GS
- dependable hydraulic pump for quick lifting & smooth lowering.
- adjustable push rod for extra support & easy maintenance
-strong reinforced "C" channel fork for heavy loads.
- sealed stainless steel ball bearings throughout
- low temperature hydraulic oil
3. Wesley International® Single Fork Pallet Trucks 3


Capacity: 3000 lbs.
- designed to lift and move loads where the fork opening is as narrow as 6 1/2". Pallet Mule's solid steel stabilizer bar combined with caster wheels makes for easy steering and load stability.
- Load stabilizer bar with casters for ease of steering and stability.
- Heavy duty fork material for maximum strength.
4. ML3348L : 4-way standard GMA pallet entry with low profile 4
- Capacity: 3,300 lbs.
- 33" x 48" 4-way standard GMA pallet entry with a low profile 1-3/4" lowered height.
- heavy-gauge reinforced frame with a durable powder coat finish.
- articulating steering wheels with lubricated ball bearings for smooth rolling, and a 270 degree steering arc for easy maneuvering.
- tough, long-lasting steel load rollers, polyurethane iron core steer wheels, and tapered fork tips with steel ramps provide trouble-free pallet entry and exit.
- heavy-duty hydraulic unit with an integrated cylinder and leak proof airless pump. and grease
- fittings at all pivot points to reduce wear and tear.
- Three-position handle control lever provides fingertip control of all hydraulic system functions with the handle in any position
- Continuous seam welds on frame for strength and durability
- Additional foot control duplicates lowering funtion control
- Self-contained rebuildable hydraulic system
- Formed fork for added strength and durability
- Steel reinforced plate strengthens frame connection and keeps forks parallel.
- Formed steel entry slide diverts debris and guides pallet truck into pallet.
6. King Pallet Jack 2748JB 6

Fork dimensions: 27" x 48"
Capacity: 5500 LbsLowered Height: 2.9"
Standard Pallet Jack with Optional Load Backrest in Poly Wheels.
Sources:
1- http://www.materialflow.com/Vestil-Pallet-Jacks.htm#WNPJ
2- http://www.mightylift.com/item.asp?invky=9131999
3- http://www.pallet-jack.org/Wesley-Pallet-Jacks-Single-Fork.htm
4- http://www.mightylift.com/item.asp?invky=7540246
5- http://www.pallet-jack.org/Bishamon-Pallet-Jacks.htm
6- http://www.pallet-truck-kingdom.com/pallet-trucks-s/3.htm
Industrial Conveyors

Industrial conveyors are horizontal, inclined, declined or vertical machinery that are widely used in food processing, packaging, assembly operations and other applications. It helps to transport goods at a controlled rate, creates efficiency and optimizes operations in the distribution centre and warehouse.
There are many types of conveyors available in the market with varying applications and designs to cater for specific operations. Depending on the materials or goods to be transported, the conveyors can be customized for different material handling needs. It can carry unit or bulk loads, and located overhead or on the floor. The items can be transported on belt, rollers or wheels. Examples of some basic types of conveyors are mentioned below:
· Non-powered conveyor
- Skate wheel conveyor
- Roller conveyor
· Powered Package Handling Conveyor
- Belt conveyor
- Roller conveyor (line-shaft, chain-driven, belt-driven, motorized)
· Powered Pallet Handling Conveyor
· Sorting Conveyor
Non-Powered Conveyor
 A skate wheel conveyor requires little energy for the wheels to spin independently which enables the product to maintain its momentum and speed. It is suitable for transporting products with flat and smooth bottomed surfaces such as cartons and trays.
A skate wheel conveyor requires little energy for the wheels to spin independently which enables the product to maintain its momentum and speed. It is suitable for transporting products with flat and smooth bottomed surfaces such as cartons and trays. Powered Package Handling Conveyor
 To facilitate the flow of packages and other relatively small items, belt conveyor and roller conveyor are well suited and able to cater to the needs.
To facilitate the flow of packages and other relatively small items, belt conveyor and roller conveyor are well suited and able to cater to the needs.What is a belt conveyor?
A belt conveyor runs on two end pulleys and it has a continuous loop of material that rotates around it. It usually consists of two layers of material. The under layer which is known as carcass provides the strength to start and move the loaded belt, while the over layer is called a cover which protects the carcass from any damage.
Belt conveyor comes in many varieties and the most popular and common ones are flat belt conveyor, trough belt conveyor and magnetic belt conveyor.
1. Flat Belt Conveyor
 It is normally used for carrying unit light and medium weight loads like bottles, boxes, or other packaged materials between operations, departments and floors. The friction between the belt and the load is able to adjust the goods into the right place on the conveyor without some unnecessary bumps. It also avoids smooth accumulation, merging and sorting on the belt. It is suitable when an incline or decline is included in the conveyor path and the adjustable angle belt conveyor can also be used.
It is normally used for carrying unit light and medium weight loads like bottles, boxes, or other packaged materials between operations, departments and floors. The friction between the belt and the load is able to adjust the goods into the right place on the conveyor without some unnecessary bumps. It also avoids smooth accumulation, merging and sorting on the belt. It is suitable when an incline or decline is included in the conveyor path and the adjustable angle belt conveyor can also be used.2. Troughed Belt Conveyor
 It is an efficient means to transport bulk materials such as concrete, ore and coal. They are built to contain the items on the belt without spilling over the edges. Trough angle selection of 20, 35 or 45 degrees should be adjusted with the flow characteristics of the product.
It is an efficient means to transport bulk materials such as concrete, ore and coal. They are built to contain the items on the belt without spilling over the edges. Trough angle selection of 20, 35 or 45 degrees should be adjusted with the flow characteristics of the product.3. Magnetic Belt Conveyor
 The belt consists of a magnetic slider bed or magnetic pulley which will help to attract the ferrous objects to the belt and overcome any angle of incline or decline. With the help of magnetic forces, the ferrous materials can be moved vertically, upside down and around corners.
The belt consists of a magnetic slider bed or magnetic pulley which will help to attract the ferrous objects to the belt and overcome any angle of incline or decline. With the help of magnetic forces, the ferrous materials can be moved vertically, upside down and around corners.Roller conveyor
Roller conveyors are suitable for accumulating loads, merging and sorting of materials. It can be categorized into four main types as shown below.
1. Line shaft conveyor
The conveyor is powered by a drive shaft running under the rollers with O-rings connecting the shaft to the rollers. When the motor turns the shaft, the shaft turns the rollers.
2. Chain-driven roller
The conveyor is designed with two sprockets welded to the end of the rollers connected to a chain under the roller bed. When the motor moves the chain, the chain moves the rollers.
3. Belt-driven roller
The conveyor is driven by a belt running under the top rollers. Similarly, when the motor moves the belt, the belt moves the rollers.
4. Motorized roller
Motorized conveyor is divided into small zones, and the rollers at each zone are connected by O-ring. The internal motor that is installed in at least one roller of each zone will turn the motorized roller and the other rollers in the same zone as well.
Powered Pallet Handling Conveyor
Pallet conveyors are typically either a roller conveyor or chain conveyor, or even a combination of these two types of conveyors which is able to carry heavy loads such as pallets and drums.
The video below is an example of a pallet conveyor system of friction rollers. It is designed in a flexible layout where straight tracks are combined, and demonstrated how junction turns and cross over of pallets can be achieved.
Sorting Conveyor
A sorting conveyor can be used for assembling items or cartons, by identifying and classifying the different products, and transport them to the respective points.
In a sorting conveyor system, it consists of four main steps which are merge step, induction step, sorting step and takeaway step.
1. Merge
The merge step refers to the combination of different and various kinds of conveyors like skewed rollers or belts. It consists of multiple infeed lines, and it will lead to the main conveying line where the sorting of items will take place.
2. Induction
In the induction step, it emphasize on gap control so as to identify the products and sort them accordingly. It can be done by controlling the speed of belts, or tracking the location of the products by using bar code scanners.
3. Sorting
In the sorting process, various devices like push diverter, deflector, rake puller and pop-up rollers and wheels are used to control and facilitate the direction movement of the products. Some examples of devices are shown as below:
- Pop-up device

The rollers are pop up above the surface of conveyor to divert the direction of the product. They are available in the right or left hand direction and they are able to sort up to 50 times per minute.
- Deflector
 A deflector is like a movable arm which deflects, push or pull a product to a specific direction.
A deflector is like a movable arm which deflects, push or pull a product to a specific direction.
A push diverter does not come in contact with the conveyor but it functions like a deflector which pushes the product to the desired location.
4. Takeaway
Finally, the last step is takeaway which is to move the sorted products by using either using powered or non-powered (gravity) conveyors.
The video below is an example of a high speed package sorting conveyor system in a distribution centre which demonstrates how the system operates and the efficient use of sorters.
Sources
Industrial Conveyor
http://www.mmh.com/article/CA6509899.html#8
http://info.lu.farmingdale.edu/depts/met/ind315/conveyors.html
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ljppe_Rn1rk
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SMEQgGcl1ik
Belt Conveyor
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conveyor_belt
For more information on other types of conveyors http://www.ise.ncsu.edu/kay/mhetax/TransEq/Conv/index.htm#Flat%20belt%20conveyor
Forklift
Another equipment that is commonly used in the distribution centre is forklift.

This is normally done by means of steel forks inserted under the load. Forklifts are most commonly used to move loads stored on pallets.
It is powered using liquefied petroleum gas – petrol or diesel fueled internal combustion engine or an electric motor(s) either direct current or alternating current powered by either battery or fuel cells.
Unlike cars, forklift is normally reared – steer.
On top of the control to rise and lower the prong, the operator can tilt the mast to compensate for a load’s tendency to angle the blades toward the ground and risk slipping off the forks. Tilt also provides a limited ability to operate on non-level ground. Furthermore, a number of machines allow the operator to shift the tines and backrest sideways, permitting the tines to be rotated. In addition, several machines offer a hydraulic control to shift the tines together or apart, which enable the operator to automatically adjust the differently sized load from the vehicle.
Forklift trucks are available in many variations and load capacities. The following are the several types which are commonly used in a distribution centre.
1. Empty container handler
2. Full container handler
3. Conventional forklift
4. Heavy lift
5. Side Loading
Currently, there are four companies dominating the counterbalanced forklift market in terms of worldwide sales. They are:
1. Toyota Industries Corporation
2. KION Group
3. Jungheinrich
4. NACCO Industries, Inc.
Empty Container Handler
The first type of forklift that we are going to touch on is empty container handler.
This equipment has a maximum capacity of 8 ton and able to do 7 high stacking for container with height of 8 feet. The main fuel used to power this machine is diesel.
Machine dimension: 260” x 163”
This is a masted empty container handler with especially high visibility. It has a maximum capacity of 9 ton and 9 stack - high visibility. It is also powered using diesel.
Full Container Handler

This full container handler has a maximum capacity of 45 ton and is able to perform 6 high stacking for 8 feet – high container. Machine dimension: 333” x 165”

This is a container handler with integrated container spreader. Its maximum capacity is 7 ton with maximum number container stacking of 4. Machine dimension: 205” x 114”
Conventional (I.C.E)
 This is an articulated narrow aisle forklift. It is compatible with a number of application specific attachments including side shift and telescopic forks for double deep pallet systems.
This is an articulated narrow aisle forklift. It is compatible with a number of application specific attachments including side shift and telescopic forks for double deep pallet systems.Machine dimension: 111” x 59 “

This is a Gasoline / petrol powered machine with capacity of 3.5 ton. Machine dimension: 112.6” x 50.8”
 This is powered using LP gas / natural gas. It has high visibility and the highest maximum lift height compared to the other two models of the conventional forklifts. Machine dimension: 104.7” x 47.8”
This is powered using LP gas / natural gas. It has high visibility and the highest maximum lift height compared to the other two models of the conventional forklifts. Machine dimension: 104.7” x 47.8”
Heavy Lift
 This machine has one of the highest load capacities of 50 ton. Its forward and reverse speed is programmable. It has power tilt function as well as air ride suspension. It is using electronic hydraulic control system. It is equipped with scale, overload protection, fire suppressing and automatic lube system as well as emergency steering.
This machine has one of the highest load capacities of 50 ton. Its forward and reverse speed is programmable. It has power tilt function as well as air ride suspension. It is using electronic hydraulic control system. It is equipped with scale, overload protection, fire suppressing and automatic lube system as well as emergency steering.Machine dimension: 291” x 147.5”
 This forklift has multiple capacities based on the amount of counterweight used. The maximum load of capacity is 10.89 ton for 48” of lift or below. For lift of 48” and above, the maximum load of capacity is 81.7 ton
This forklift has multiple capacities based on the amount of counterweight used. The maximum load of capacity is 10.89 ton for 48” of lift or below. For lift of 48” and above, the maximum load of capacity is 81.7 ton












